In this article, we will discuss the Ameican sweetgum allergy (Liquidambar styraciflua) and how and when this tree’s pollen spreads.
| American sweetgum (Liquidambar styraciflua) | Pollen allergy profile |
|---|---|
| Pollen season | Spring. Generally, Mar-15th to Apr-15th. |
| Pollination type | Wind transported. Each tree releases a lot of pollen into the air. |
| Cross-reactivity with other pollen | Other trees of genus Liquidambar but American sweetgum is the only tree commonly found in the US. The other species, e.g. Chinese sweetgum, are mostly found in Asia. |
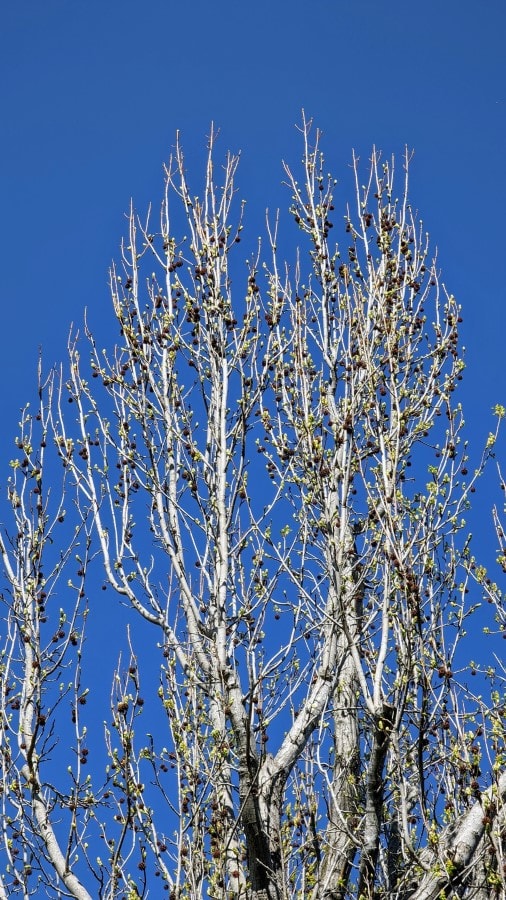
| Pollen source | Green male catkins (flowers) that grow in the shape of an erect conical inflorescence (see pictures below.) |
| Gender | Monoecious: The tree has separate male and female flowers on the same tree. |
| Fruit | Spikey green, golf-ball-sized fruit that eventually turns very dark brown (see pictures below.) |
| Bark | The bark is grey or dark brown with deep vertical or slanted ridges (see pictures below.) |
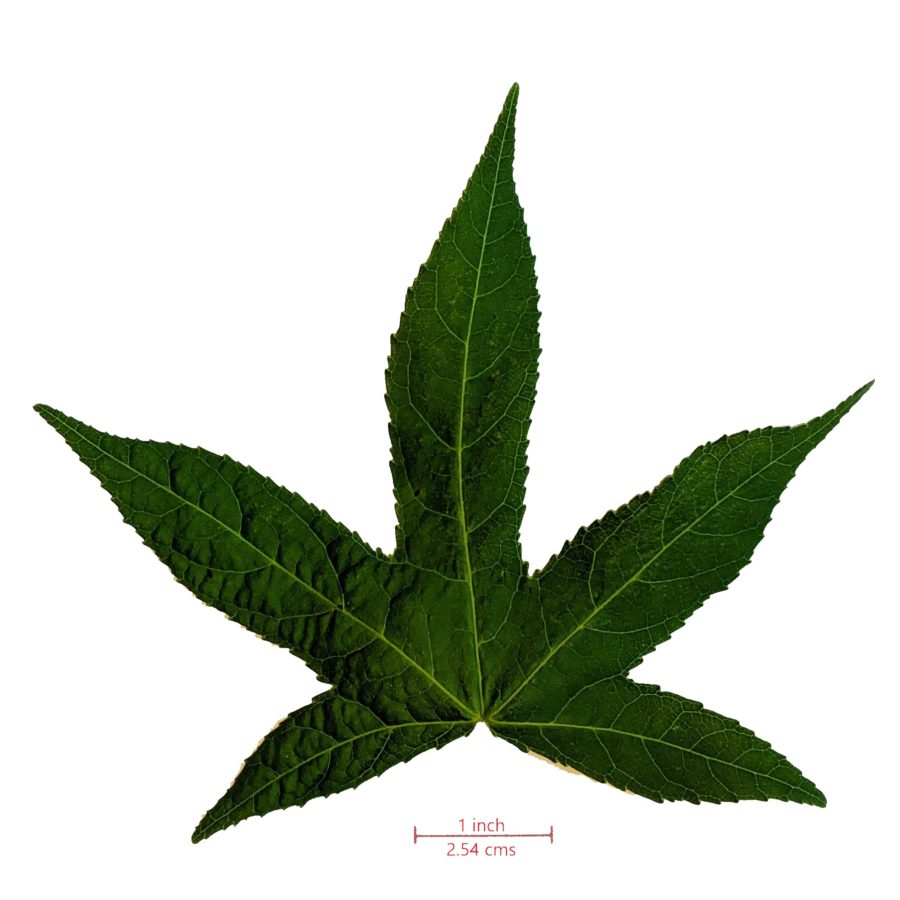
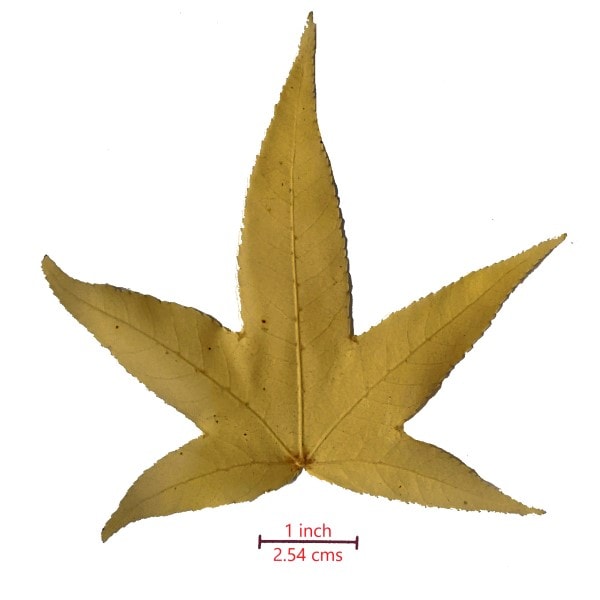
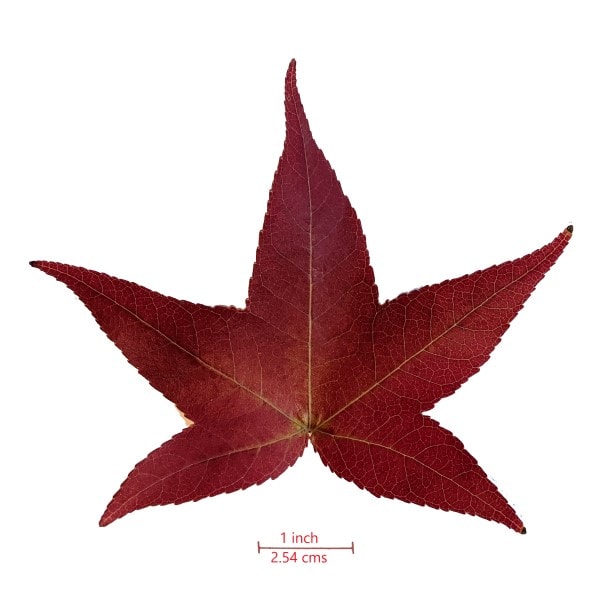
| Leaves | Star-shaped generally with five lobes, but three or seven lobes possible (see pictures below.) |
How to identify American sweetgum (Liquidambar styraciflua) trees?
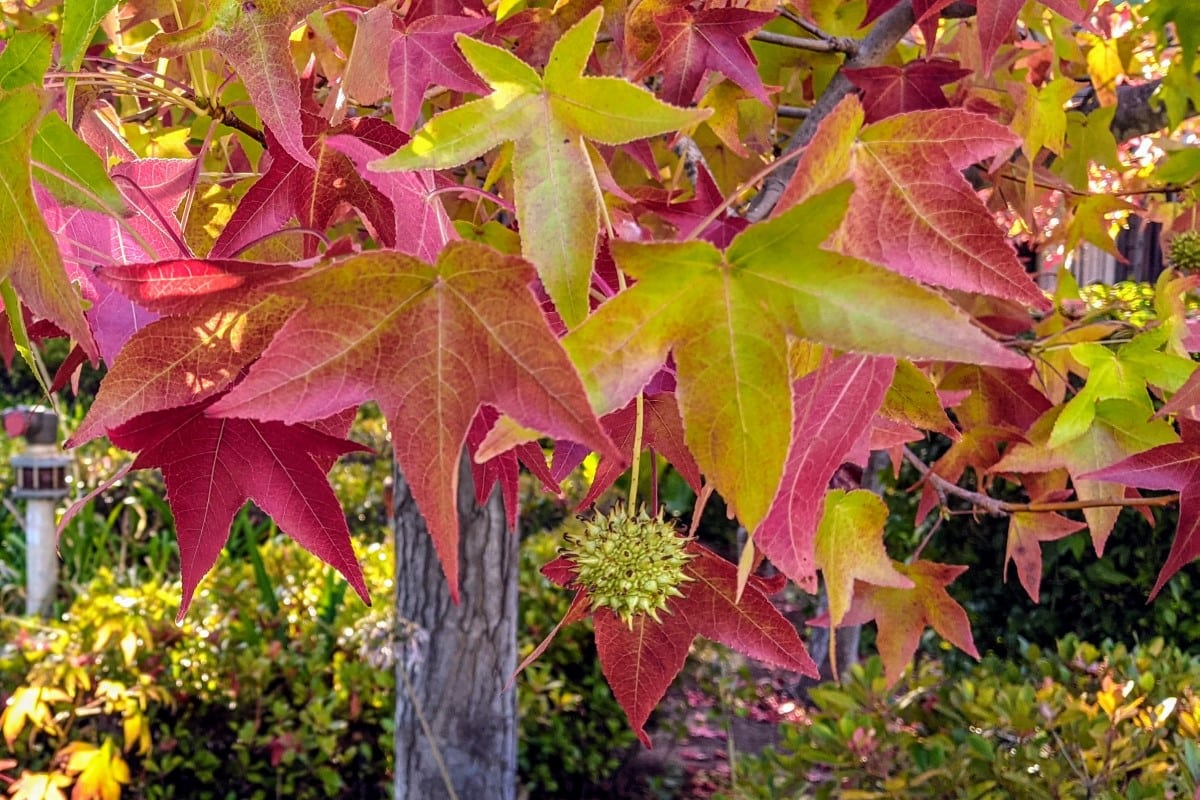
American sweetgum, also known as redgum or star-leaved gum, is widely grown as a street tree in California and pretty much in all states east of Texas[1]. The tree is native to the United States and is particularly beautiful in autumn when leaves turn yellow, red, or purple.
A sweetgum tree, or Liquidambar styraciflua, can be easily identified by its spiky golf-sized fruit and five-lobed star-shaped leaves. The young fruit is green in color during spring but changes to dark brown by winter.
Sweetgum is a deciduous tree and it loses its leaves in autumn but the spikey fruit remains on the tree through winter.
Fruit
Since the American sweetgum keeps its fruit on the branches year-round, it is a good tree identification marker.
The American sweetgum tree’s fruit is the of a golf ball and is covered with pointed spikes. It is green in color when young but it turns dark brown upon maturation.
During winter, the tree loses its leaves but the dark brown spikey fruit remains on the tree.
Leaves
The star-shaped, serrated leaves of the American sweetgum tree generally have five lobes but three or seven lobes are possible. Each leaf blade can be 3 to 8 inches long.
The leaves are green during spring and summer and change to yellow, red, and purple during autumn.
The sweetgum leaves can be confused with maple’s, but, the fruits of the two trees are very different so if you are not sure about leaves, use fruit for the identification (discussed in the next section)
bark and trunk.
The American sweetgum tree bark has deep verticle or slightly slant ridges. The color of the bark ranges from gray to dark brown.
A single trunk generally rises straight up 8 to 10 feet before branching out. The trunk is 1 to 4 feet wide.
When do the American sweetgum trees release pollen?
American sweetgum releases pollen during early spring. In California, it is among the first trees to release pollen in March. In cooler climates of the East Coast, the tree releases pollen in April.
The tree releases most of its pollen from mid-morning to early afternoon. Our air sampler in Burlingame, California catches most of the pollen between 11:00 am and 2:00 pm between March-15th and April-15th.
The tree has a relatively short pollen release cycle of three to four weeks.
The pollen schedule for the American sweetgum can vary by one to two weeks each year depending on the length and severity of the preceding winter. If you live in the San Francisco Bay Area and suffer from sweetgum allergies, we do regular air sampling and tree inspections to provide you with reliable pollen updates.
How does American sweetgum pollen spread?
Sweetgum allergies are caused but it’s wind-transported pollen. During spring, the tree releases a copious amount of pollen in the air and wind can carry the pollen many miles.
The tree generally has a very short pollination cycle of three to four weeks, but it does release large amounts of pollen in that short period.
Sycamore (Platanus) tree also releases pollen pretty much at the same schedule as sweetgum.
What does American sweetgum pollen look like?
The male flowers fall on the ground upon maturation and you can see pollen in the form of a fine yellow powder spilling out of it. However, the individual grains of pollen are invisible to the eye when they are airborne.
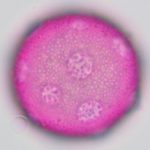
The pollen grain is spherical, about 40 microns in diameter (0.04 mm), and has 18-20 pores. Liquidambar styraciflua pollen: Periporate with freckles on the pores.
To see the pollen of other plants and trees, visit our pollen library.
How big are sweetgum trees?
An American sweetgum tree can grow to 75 feet tall and 45 feet wide but most street trees are trimmed and do not grow past 50 feet tall.
What do American sweetgum flowers look like?
The American sweetgum pollen is produced by its male flowers (catkins). Fortunately, these flowers have a very short life – they start developing in winter, release pollen in March and April and then fall off the tree by the end of May.
Each conical-shaped inflorescence is about one inch long and contains about 10 small ball-shaped green flowers.
The flowers are easy to spot in spring because they appear before the new leaves. The tree at this stage only has old fruit and new green catkins.
The female flower is a small ball-shaped flower that hangs loose on the branches. When successfully pollinated, it turns into the spikey round fruit that stays on the tree for over a year before it falls off[2].
How to know if an American sweetgum tree is releasing pollen?
If you suffer from sweetgum allergies, you can learn about its pollination cycle to know when to take precautions. When the male catkins are green and glossy during late winter, they are still not mature enough to release pollen. However, when they turn a little yellowish-brown and powdery, they are mature enough to be releasing pollen.
Each catkin is capable of releasing millions of pollen into the air!
If you see some catkins on the tree and some under the tree with yellow dust around them, it means the tree is releasing pollen in large quantities.
Once the pollination has started, all-male catkins eventually fall off the tree in three to four weeks. However, the pollen from catkins on the ground can still become airborne when disturbed by leaf blowers or street cleaners.
If you are allergic to the sweetgum pollen, take precautions until the catkins from the ground disappear either by cleaners or rains.
You can learn a lot more about pollen allergies and how to avoid them in my pollen allergy guide.
Do all American sweetgum trees release pollen?
During the early spring, when the American sweetgum trees blossom, each tree will have both male and female flowers on the same tree. The male flower is responsible for releasing pollen. This means all healthy American sweetgum trees will produce pollen if they are mature enough to do so.
Luckily the sweetgum tree has a short pollen release cycle of three to four weeks. It starts in mid-March and concludes by mid-April.
The summary of American sweetgum pollen allergy.
Although American sweetgum allergies are not common, the tree releases large quantities of pollen in the air during spring. However, some clinics and pollen forecasting websites ignore this pollen. Thus, the allergenicity of this pollen is not as well established as some other spring pollinating trees like birch (Betula), Sycamore (Platanus), Oak (Quercus), Mulberry (Morus), Walnut (Juglans), Alder (Alnus), Ash (Fraxinus), and Hackberry (Celtis).
Sources
- https://plants.usda.gov/DocumentLibrary/plantguide/pdf/pg_list2.pdf
- https://naturewalk.yale.edu/trees/altingiaceae/liquidambar-styraciflua/american-sweetgum-46
References
- Allergy Plants by Mary Jelks, M.D.
- Plant identification terminology by James G. Harris and Melinda Woolf Harris (Second Edition)
- Sampling and identifying pollens and molds by E. Grant Smith
We study trees and their pollen by doing regular tree inspections and air sampling. The pollen picture is taken in our aerobiology lab using an Olympus compound microscope.














I am confused and confounded by this Sweetgum Tree Stump that was in my yard near my windows and it has started sprouting from the stump & really shooting up from it’s horribly wide root system, The previous owner did not cut and kill the tree with any noticeable sure fire method.
So right now I had my window opened for the last 35 or more minutes and my eyes for some reason are burning. The skin around my eyes feel like its burning I do not know if it is from these tall sprouts.
I don’t remember allergies to anything that was occurring with this tree in the Spring. You have pictures of the immature leaf and pod system covered w/ fresh pollen, but that for me went unnoticed here. I do not know if this is a regional variety , but I see the mature trees & sprouts now everywhere. I am not from NC or the east coast so this tree was never on my radar or possibly affecting me. It has these Corona virus looking pokey brown ball pods that fall everywhere at a different time of the year. Please explain what this variety causes in the way of allergies. I am having someone naturally kill this sprawliing stump next week . It will apparently take numerous doses of high nitrogen fertilizer and salt? &/or vinegar (have to read instructions again) into a ditch that has to be dug around this stump and then covered to impair photosynthesis….
Hi Lisa – Sweetgum produces pollen during spring, so it is unlikely that your symptoms are coming from Sweetgum pollen. Allergies are a complex subject and it is possible that you may be allergic to some other aspect of that tree stump (spores from any fungal growth on or around the tree, or residual chemicals from previous attempts to impair the tree), or something entirely different. I would recommend seeing an allergy doctor for further guidance and testing. Sudhir