In this article, we will learn to identify Hackberry trees (scientific name: Celtis) as well as how and when their pollen spreads.
| Hackberry or Sugarberry (Genus: Celtis) | Pollen allergy profile |
|---|---|
| Pollen season | Spring |
| Pollination type | Wind-pollinated |
| Cross-reactivity with other pollen | Not known |
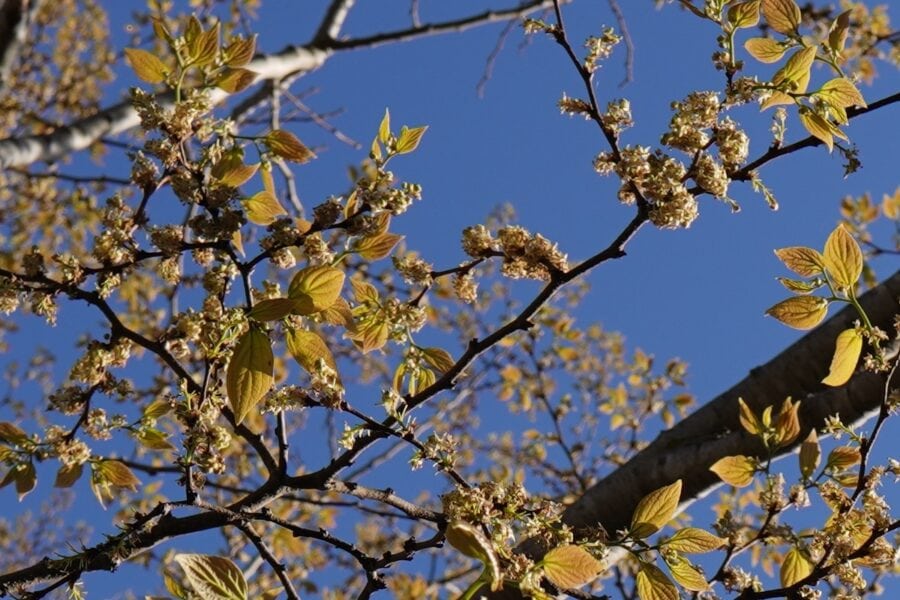
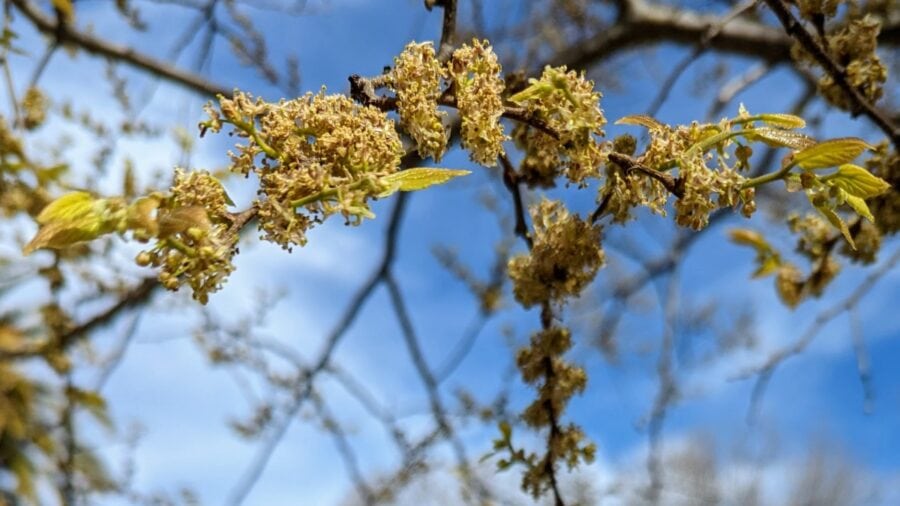
| Pollen source | Yellow cotton ball-like flowers |
| Gender | Monoecious: Separate male and female flowers bloom on the same tree. |
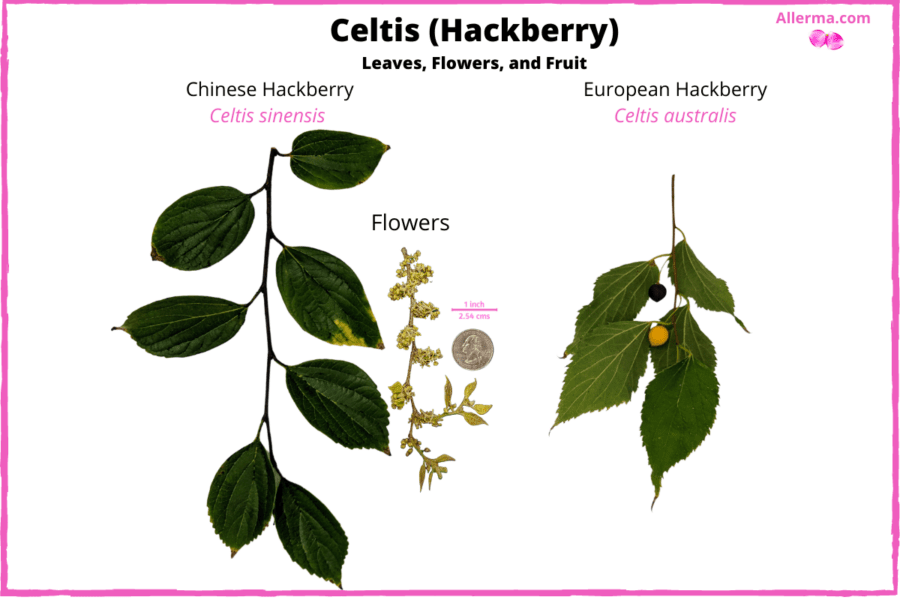
| Leaves | Saw-tooth edges on leaves that grow alternately on the twig |
| Fruit | Green, peanut-sized, berry-like drupes that turn orange or purple by fall. |
How to identify a hackberry (Celtis) tree?
The two species, Celtis australis (European hackberry) and Celtis sinensis (Chinese hackberry), that we cover in this article, are both common as introduced decorative trees in California. However, other species like Celtis laevigata (also known as sugarberry), grow across the US as native plants [1].
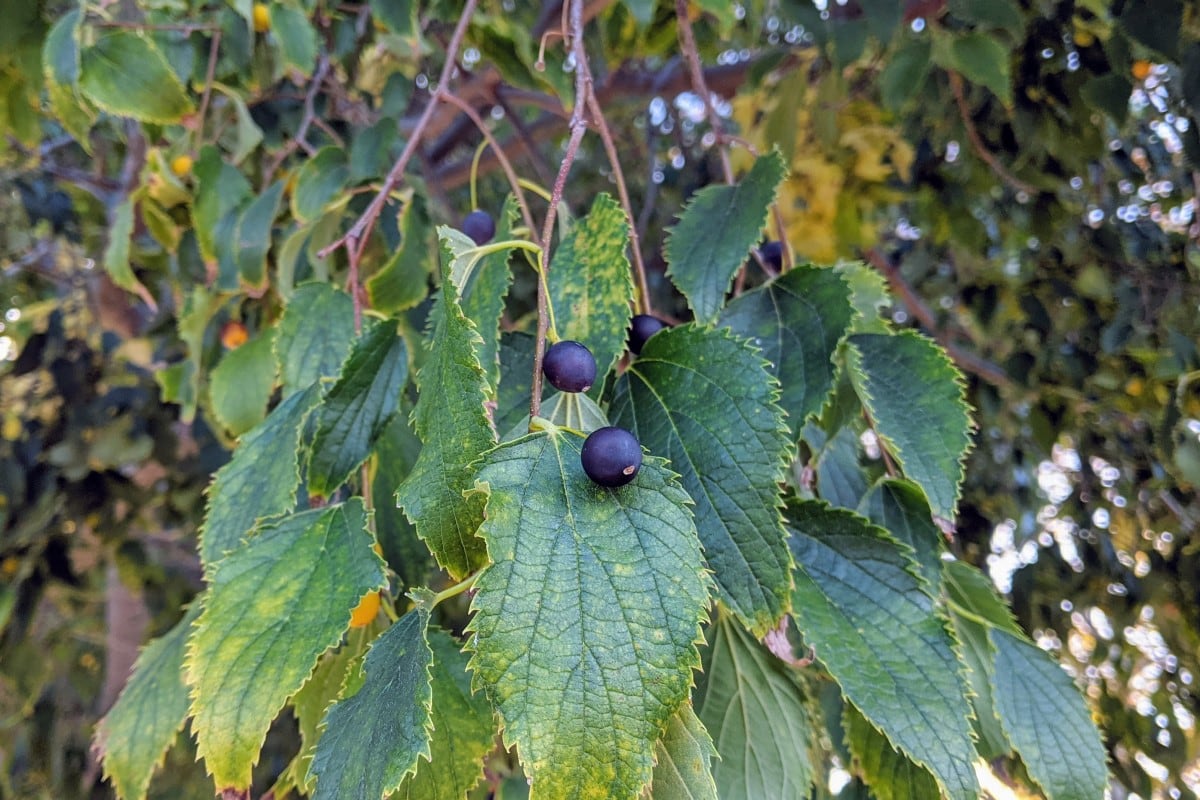
Hackberry, Genus: Celtis, has green leaves with sharp sawtooth-like edges. In summer, it produces small green berry-like fruit, which ripens to orange color by fall and eventually turns purple.
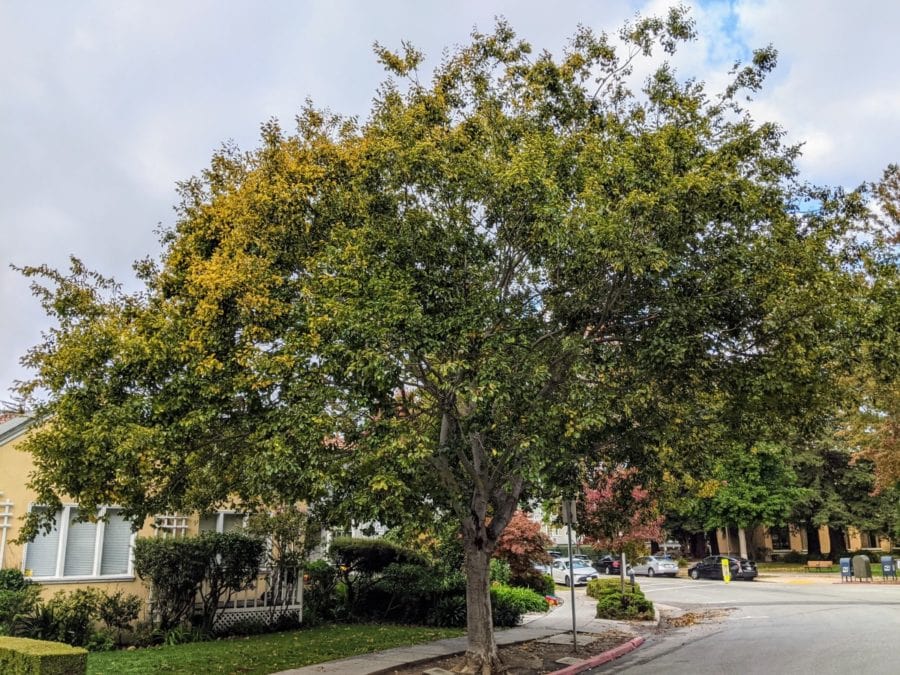
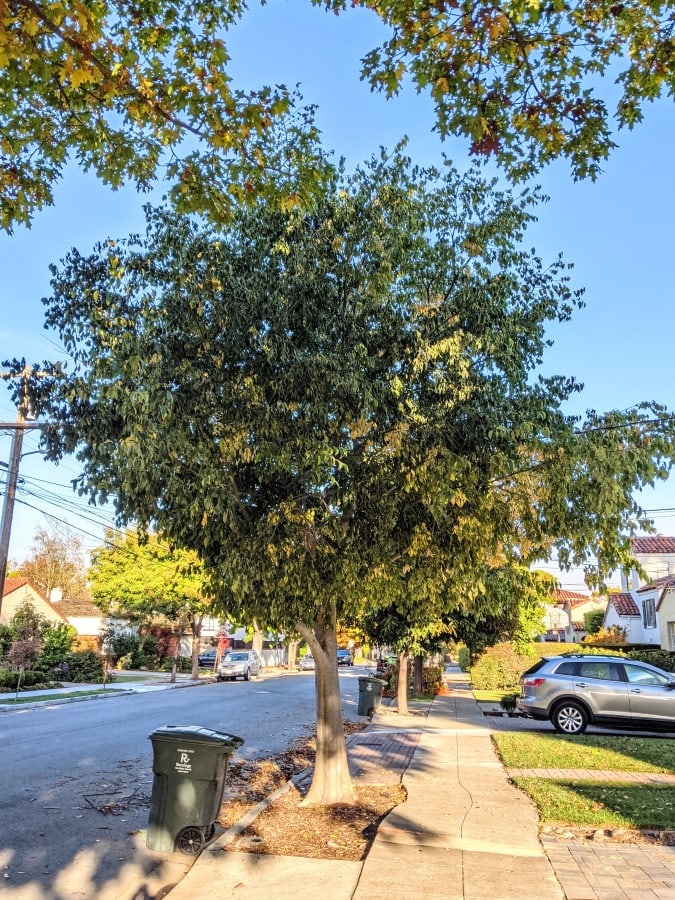
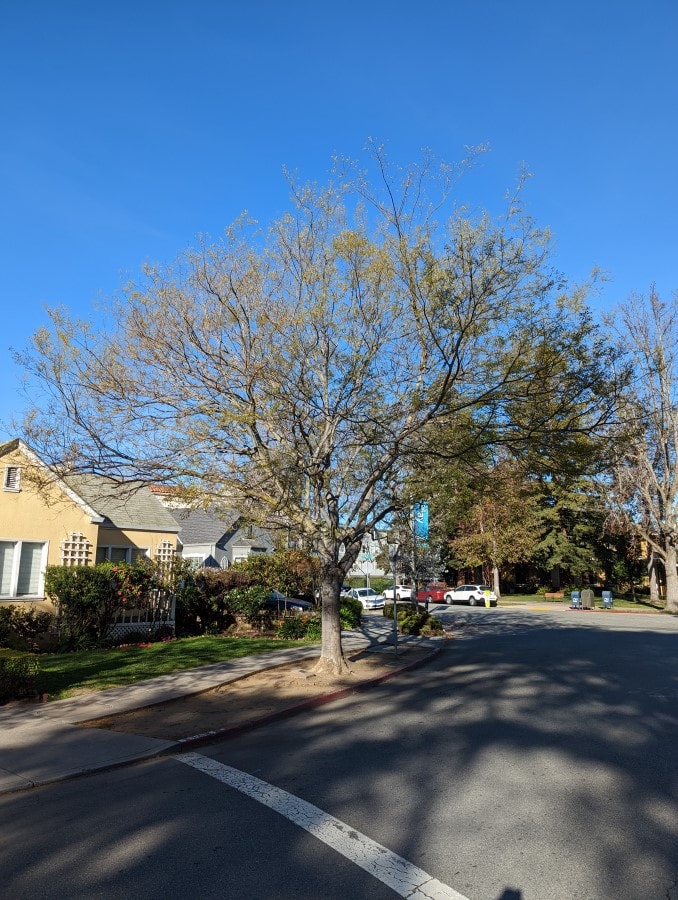
Tree shape and size
Most Celtis trees grow up to 25 to 30 feet, but it is possible for them to be 60 feet tall [2].
The trees have wide lush canopies.
Here are pictures of Chinese hackberry and European hackberry.
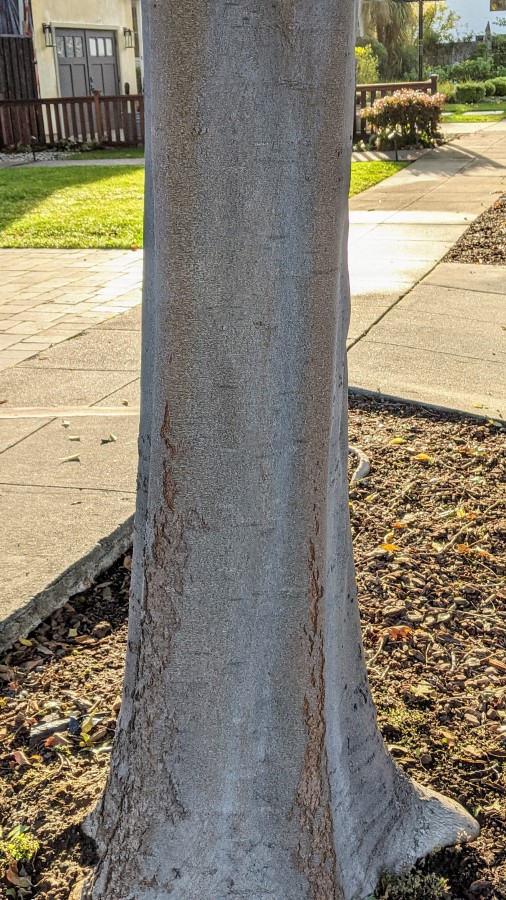
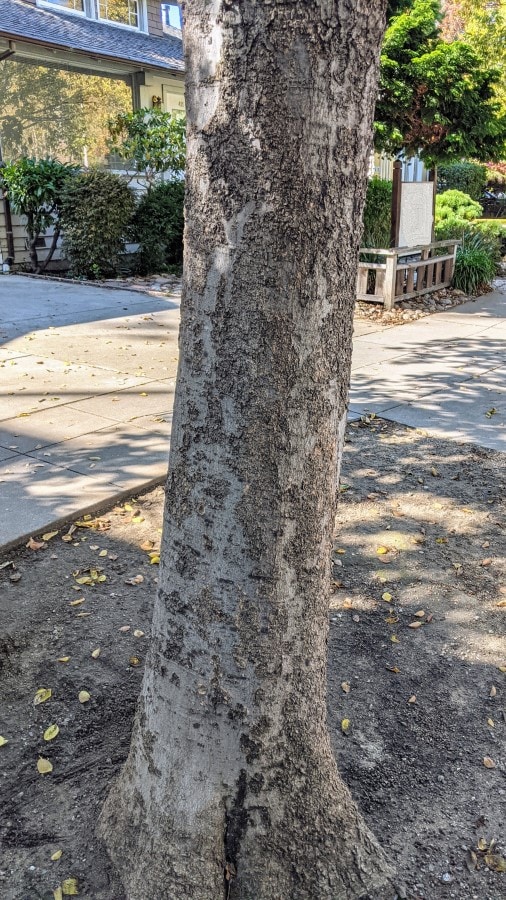
Tree bark and trunk
Celtis trees generally have a single trunk rising from the ground. The young tree has a smooth light grey bark, but as the tree matures, darker grey cork or wart-like scales start to appear.
The trunk is about one to two feet in diameter at eye level.
During which months hackberry (Celtis) releases pollen?
Celtis releases pollen during early spring.
In the San Francisco bay area, Celtis pollen is found in our air surveys from Mar-15th to Apr-30th.
The Chinese hackberry blooms first around March-15th and it releases pollen for about four weeks. The European hackberry blooms around April-1st and releases pollen until Apr-30th.
Depending on the temperature and rainfall of the preceding winter, the actual pollination period could shift by one to two weeks each year. By learning to inspect trees for signs of spring flowering, you can learn to manage your allergies better.
However, if you live in the San Francisco Bay Area, you have an easier way out! I do regular tree inspections and air sampling in the area to provide reliable pollen updates on our website
How to know if Celits is releasing pollen?
During spring, small yellow-green clumped together flowers emerge before leaves. The tree looks pretty bare when flowers emerge because leaves are still absent or really small. The pollination stops when the tree turns lush green by April.
How does hackberry/sugarberry (Celits) pollen spread?
Hackberry/sugarberry (Celits) releases its pollen in the air and wind can carry the pollen many miles.
Since the tree is widely present in the mainland USA, its pollen is expected to be in the air surveys everywhere during spring.
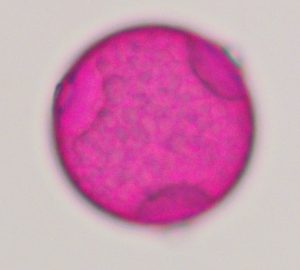
What does hackberry/sugarberry (Celtis) pollen look like?
The pollen is around 30 micrometers (0.03 mm) in size and has three pores, each pore has some thickening of the surface around it. Celtis pollen: Triporate, aspidate.
To see the pollen of other plants and trees, visit our pollen library.
Celtis, Hackberry, Sugarberry allergy summary
Hackberry/Sugarberry (Genus: Celtis) trees release pollen in the air during spring and are present across the US. They are not commonly tested for allergies by clinicians, so, their role in spring hay fever is not fully understood.
The other trees that release pollen alongside Celtis during spring are Birch, American sweetgum, oaks, and Sycamores.
Sources
References
- Allergy Plants by Mary Jelks, M.D.
- Plant identification terminology by James G. Harris and Melinda Woolf Harris (Second Edition)
- Sampling and identifying pollens and Molds by E. Grant Smith
All pictures, unless otherwise credited to another source, are taken by the author and are copyrighted material. The pollen picture is taken in our aerobiology lab using an Olympus compound microscope.